This post shows how we have used lidar data to calculate the aspect and estimate the south facing area of a rooftop.
Requirements
- QGIS - used to process the data.
- PostGIS database - to store the procuct and run some queries on it.
- Lidar data or other asc DSM - you can view coverage and download free lidar tiles from the UK’s Environment Agency here.
- Building polygon data. We used Ordnance Survey’s MasterMap for this.
Desired Product
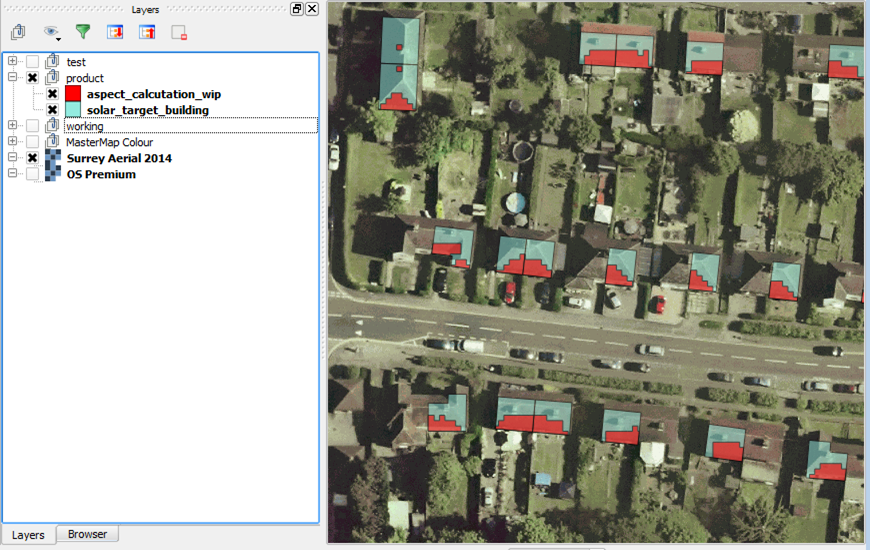
First a preview of what we can produce:
In red is the South facing aspect area of a rooftop. In blue are buildings we are interested in analysing.
Workflow Outline
- Process lidar dsm.asc into aspect rasters
- Reclassify aspect rasters to simplify values
- Polygonize the aspect rasters
- Load into PostGIS (filter out unwanted classes on import)
- Clip out features not within target building polygons
- Select features within the target building polygons, includes area sizes
- Calculate percentage of rooftop which is south facing
Workflow Screenshots
-
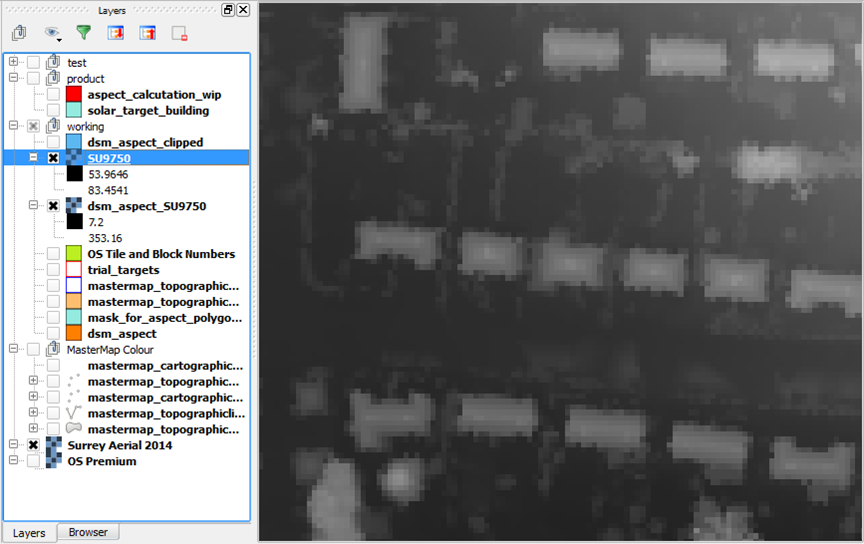
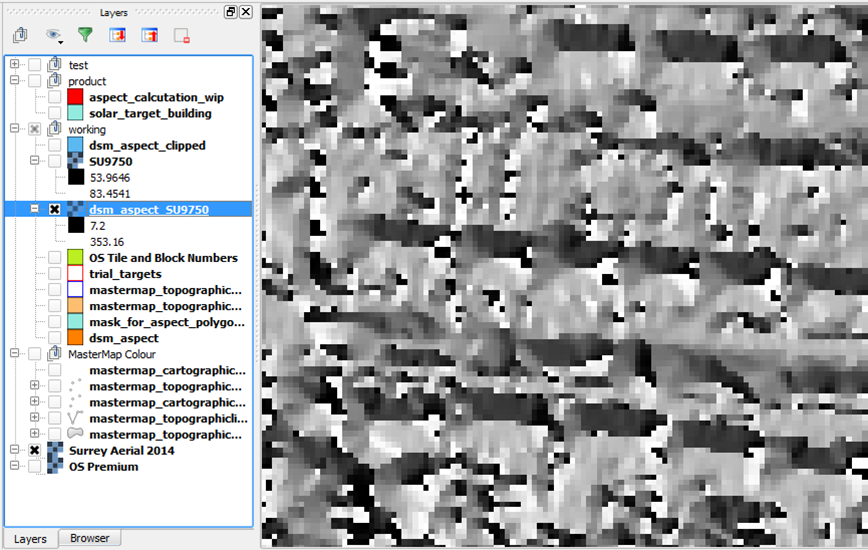
Process lidar dsm.asc into aspect rasters
Using the QGIS Toolbox: GDAL → Aspect (run in batch for multiple asc files)
Source asc file:
Output tif file:
-
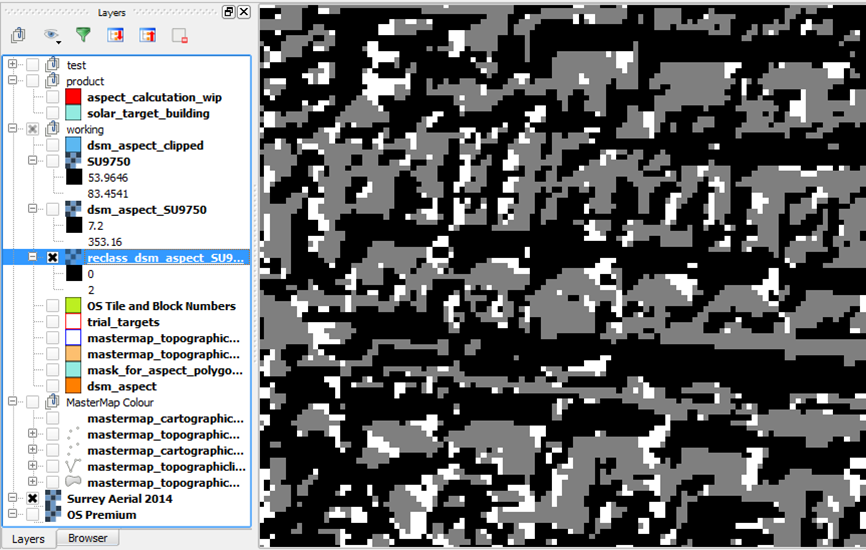
Reclassify aspect rasters to simplify values
QGIS Toolbox: Grass → Raster → Classify
This reclassification is done to set the pixel value to 1 if the aspect is between 135-225 degrees from North and 0 if it is not. Reclassifying helps speed up later processes and reduce file sizes.
-
Polygonize the aspect rasters
QGIS Toolbox: GDAL → Conversion → Polygonize (raster to vector)
This process converts rasters to vector data. We need to query the data later to calculate surface areas so converting the data to vector is useful here.
-
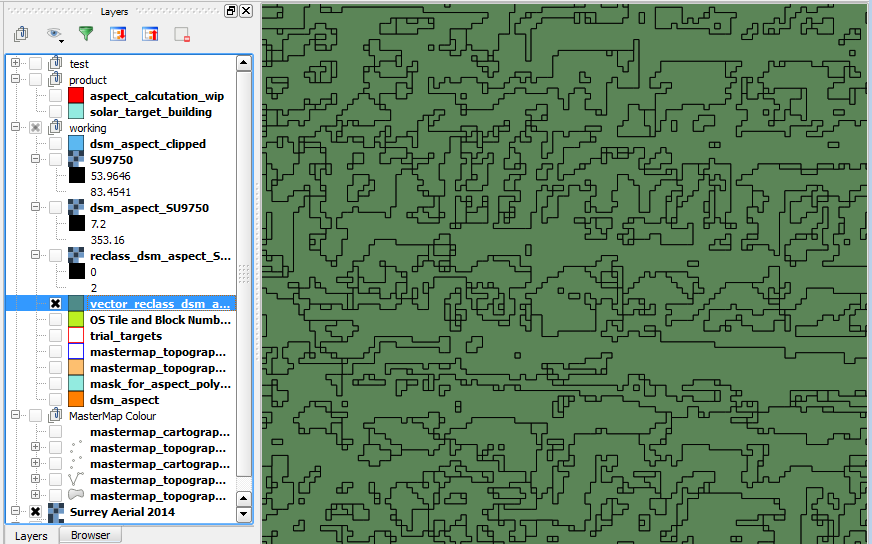
Load into PostGIS (filter out unwanted classes on import)
Importing the data to a PostGIS database allows us to run queries later on to calculate area sizes and intersections. When running the import a filter can be set to exclude features with certain values. In the below example features with a value of 0 were excluded from the import.
This leaves us with a vector layer of all South facing areas.
-
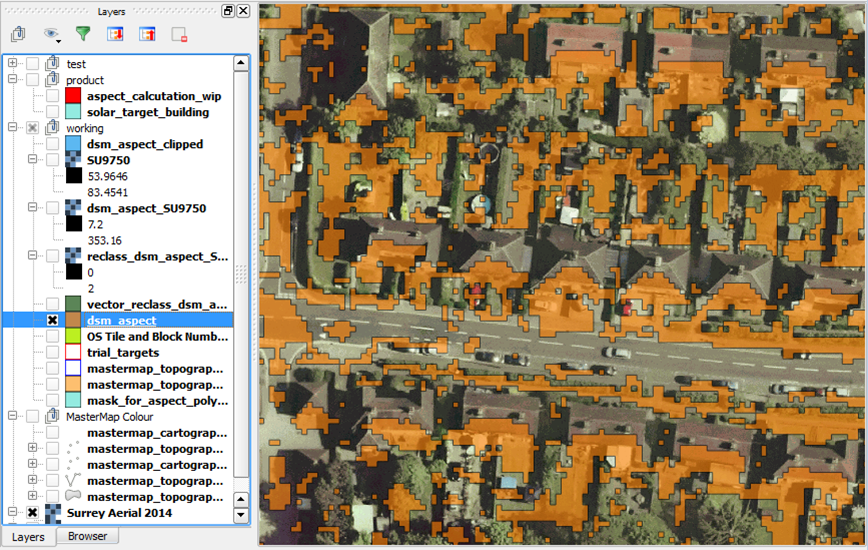
Clip out features not within target building polygons
The aspect layer is clipped to our building layer so that the surface area estimates only include the building extent.
-
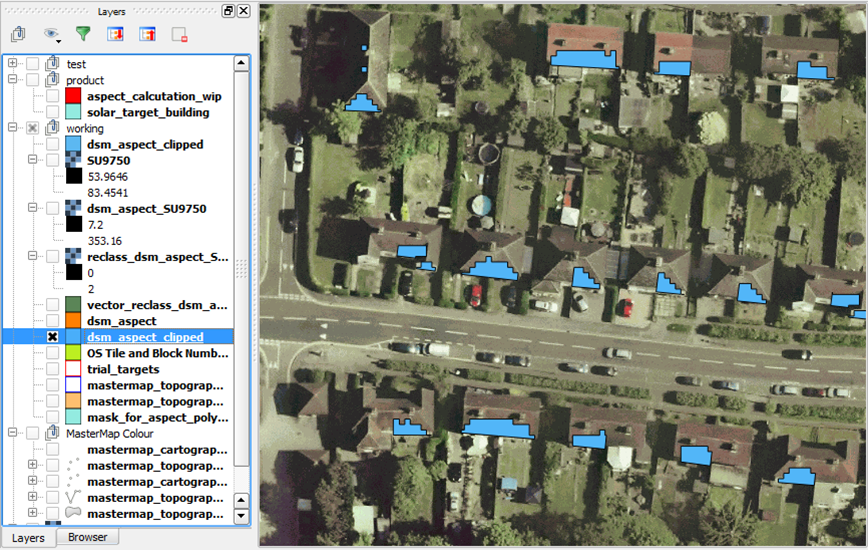
Select features within the target building polygons, includes area sizes
We also needed to split the features where they cross building polygons. We then calculated the gross surface area of the south facing aspect shapes. The PostGIS functions
1
st_intersection
1
st_area
-
Calculate percentage of rooftop which is south facing
We then calculated the proportion of the building which we estimate as South facing.
Product
Everything filtered, clipped and queried…

Credit
- Aerial imagery and lidar: © Bluesky Internation Limited
- Building polygons: © Ordnance Survey 2016. Lic No. 100019625.